
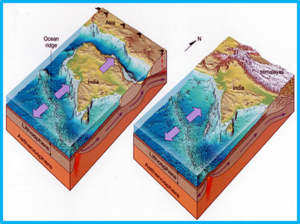
When two tectonic plates slide past each other, the place where they meet is a transform or lateral fault. This can lead to the formation of huge, high mountain ranges such as the Himalayas. Since neither plate is stronger than the other, they crumple and are pushed up. The northeast side of the Australian plate converges with the Pacific Plate. About 80% of earthquakes occur where plates are pushed together, called convergent boundaries.Īnother form of convergent boundary is a collision where two continental plates meet head-on. Sometimes the molten rock rises to the surface, through the continent, forming a line of volcanoes. The rocks pulled down under the continent begin to melt. Subduction causes deep ocean trenches to form, such as the one along the west coast of South America. When a continental plate meets an oceanic plate, the thinner, denser, and more flexible oceanic plate sinks beneath the thicker, more rigid continental plate. The Great Rift Valley in Africa, the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden all formed as a result of divergent plate motion.Ĭonvergent (Colliding): This occurs when plates move towards each other and collide. The earthquakes that occur along these zones, called spreading centers, are relatively small. Molten rock from the mantle erupts along the opening, forming new crust.

From east to west the Himalayas are divided into 3 regions, Eastern Himalaya, Central Himalaya, and Western Himalaya, which collectively house several nations and states. Examples of fold mountains include The Himalayas, The Andes, The Rockies and. Himalaya has Indo-Gangetic Plain in south, Pamir Mountains in west in Central Asia, and Hengduan Mountains in east on ChinaMyanmar border. The three main types of plate movements include:ĭivergent (Spreading):This is where two plates move away from each other. Tectonic plates are pieces of the Earths crust and the upper mantle- the. The movements of the plates help shape the geological features of our planet. Other plates include continents, and some plates include both continents and ocean. There is much debate however about the structure and geometry of this decollement surface. Some of the plates have ocean water above them. The main plate boundary fault, also called the Main Himalayan Thrust (or MHT), is the main basal decollement into which all minor faults sole. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is released as seismic waves, causing the ground to shake. Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundaries-divergent, convergent, and transform.Īs the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up. Movement in narrow zones along plate boundaries causes most earthquakes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
